RPS-BLAST 2.2.9 [May-01-2004]
Query= local sequence: htrA
(486 letters)
Database: cdd.v2.01
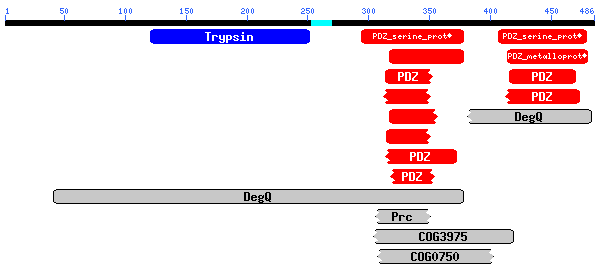
 ..
This CD alignment includes 3D structure. To display structure, download
Cn3D! ..
This CD alignment includes 3D structure. To display structure, download
Cn3D!
| |
PSSMs producing
significant alignments: |
Score
(bits) |
E
value |
| |
 |
gnl|CDD|27590 |
cd00987, PDZ_serine_protease, PDZ domain of
tryspin-like serin... |
73.8 |
4e-14 |
 |
gnl|CDD|27590 |
cd00987, PDZ_serine_protease, PDZ domain of
tryspin-like serin... |
57.6 |
3e-09 |
 |
gnl|CDD|27592 |
cd00989, PDZ_metalloprotease, PDZ domain of
bacterial and plan... |
48.3 |
2e-06 |
 |
gnl|CDD|27592 |
cd00989, PDZ_metalloprotease, PDZ domain of
bacterial and plan... |
47.5 |
3e-06 |
| |
gnl|CDD|27588 |
cd00136, PDZ, PDZ domain, also called DHR (Dlg
homologous regi... |
46.0 |
9e-06 |
| |
gnl|CDD|27588 |
cd00136, PDZ, PDZ domain, also called DHR (Dlg
homologous regi... |
39.1 |
0.001 |
 |
gnl|CDD|27595 |
cd00992, PDZ_signaling, PDZ domain found in a
variety of Eumet... |
45.6 |
1e-05 |
 |
gnl|CDD|27594 |
cd00991, PDZ_archaeal_metalloprotease, PDZ
domain of archaeal ... |
44.1 |
3e-05 |
 |
gnl|CDD|27591 |
cd00988, PDZ_CTP_protease, PDZ domain of
C-terminal processing... |
42.9 |
8e-05 |
 |
gnl|CDD|25297 |
smart00228, PDZ, Domain present in PSD-95,
Dlg, and ZO-1/2. Al... |
48.1 |
2e-06 |
 |
gnl|CDD|25297 |
smart00228, PDZ, Domain present in PSD-95,
Dlg, and ZO-1/2. Al... |
39.6 |
8e-04 |
 |
gnl|CDD|25389 |
pfam00089, Trypsin, Trypsin |
54.3 |
3e-08 |
 |
gnl|CDD|25565 |
pfam00595, PDZ, PDZ domain (Also known as DHR
or GLGF). PDZ do... |
43.0 |
7e-05 |
| |
gnl|CDD|10140 |
COG0265, DegQ, Trypsin-like serine proteases,
typically peripl... |
198 |
1e-51 |
| |
gnl|CDD|10140 |
COG0265, DegQ, Trypsin-like serine proteases,
typically peripl... |
43.7 |
5e-05 |
 |
gnl|CDD|10661 |
COG0793, Prc, Periplasmic protease [Cell
envelope biogenesis, ... |
44.6 |
2e-05 |
| |
gnl|CDD|13280 |
COG3975, Predicted protease with the
C-terminal PDZ domain [Ge... |
40.3 |
4e-04 |
| |
gnl|CDD|10618 |
COG0750, Predicted membrane-associated
Zn-dependent proteases ... |
39.8 |
7e-04 |
 |
gnl|CDD|27590, cd00987, PDZ_serine_protease, PDZ
domain of tryspin-like serine proteases, such as DegP/HtrA, which
are oligomeric proteins involved in heat-shock response, chaperone
function, and apoptosis. May be responsible for substrate
recognition and/or binding, as most PDZ domains bind C-terminal
polypeptides, though binding to internal (non-C-terminal)
polypeptides and even to lipids has been demonstrated. In this
subfamily of protease-associated PDZ domains a C-terminal
beta-strand forms the peptide-binding groove base, a circular
permutation with respect to PDZ domains found in Eumetazoan
signaling proteins. | CD-Length = 90 residues, 96.7% aligned
Score = 73.8 bits (181), Expect = 4e-14
Query: 293 GEVGILTQDLTPGLAKAFGIDEGAGALVSEVLPGSPAANAGIQPGDVIRMVDGRTVRGAS 352
Sbjct: 1 PWLGVTVQDLTPDLAEELGLKDTKGVLVASVDPGSPAAKAGLKPGDVILAVNGKPVKSVA 60
Query: 353 DVRRLVGSLPLQSKPSFQIDRASRRIE 379
Sbjct: 61 DLRRALAELKPGDKVTLTVLRGGKELT 87
 |
gnl|CDD|27590, cd00987, PDZ_serine_protease, PDZ
domain of tryspin-like serine proteases, such as DegP/HtrA, which
are oligomeric proteins involved in heat-shock response, chaperone
function, and apoptosis. May be responsible for substrate
recognition and/or binding, as most PDZ domains bind C-terminal
polypeptides, though binding to internal (non-C-terminal)
polypeptides and even to lipids has been demonstrated. In this
subfamily of protease-associated PDZ domains a C-terminal
beta-strand forms the peptide-binding groove base, a circular
permutation with respect to PDZ domains found in Eumetazoan
signaling proteins. | CD-Length = 90 residues, 85.6% aligned
Score = 57.6 bits (139), Expect = 3e-09
Query: 406 ADAEMANSPDGPGARVVVVAEGSVAAQAGLQPDDVIVALDQQPVTDVGQLLSIL--VKEH 463
Sbjct: 13 DLAEELGLKDTKGVLVASVDPGSPAAKAGLKPGDVILAVNGKPVKSVADLRRALAELKPG 72
Query: 464 ARALITVVRNGHRLFVA 480
Sbjct: 73 DKVTLTVLRGGKELTVT 89
 |
gnl|CDD|27592, cd00989, PDZ_metalloprotease, PDZ
domain of bacterial and plant zinc metalloprotases, presumably
membrane-associated or integral membrane proteases, which may be
involved in signalling and regulatory mechanisms. May be responsible
for substrate recognition and/or binding, as most PDZ domains bind
C-terminal polypeptides, and binding to internal (non-C-terminal)
polypeptides and even to lipids has been demonstrated. In this
subfamily of protease-associated PDZ domains a C-terminal
beta-strand forms the peptide-binding groove base, a circular
permutation with respect to PDZ domains found in Eumetazoan
signaling proteins. | CD-Length = 79 residues, 79.7% aligned
Score = 48.3 bits (115), Expect = 2e-06
Query: 316 AGALVSEVLPGSPAANAGIQPGDVIRMVDGRTVRGASDVRRLVGSLPLQSKPSFQIDRAS 375
Sbjct: 12 IEPVIGEVVPGSPAAKAGLKAGDRILAINGQKIKSWEDLVDAVQENP-GKPLTLTVERNG 70
Query: 376 RRIE 379
Sbjct: 71 ETIT 74
 |
gnl|CDD|27592, cd00989, PDZ_metalloprotease, PDZ
domain of bacterial and plant zinc metalloprotases, presumably
membrane-associated or integral membrane proteases, which may be
involved in signalling and regulatory mechanisms. May be responsible
for substrate recognition and/or binding, as most PDZ domains bind
C-terminal polypeptides, and binding to internal (non-C-terminal)
polypeptides and even to lipids has been demonstrated. In this
subfamily of protease-associated PDZ domains a C-terminal
beta-strand forms the peptide-binding groove base, a circular
permutation with respect to PDZ domains found in Eumetazoan
signaling proteins. | CD-Length = 79 residues, 91.1% aligned
Score = 47.5 bits (113), Expect = 3e-06
Query: 413 SPDGPGARVVV--VAEGSVAAQAGLQPDDVIVALDQQPVTDVGQLLSILVKEHARAL-IT 469
Sbjct: 6 VPGGPPIEPVIGEVVPGSPAAKAGLKAGDRILAINGQKIKSWEDLVDAVQENPGKPLTLT 65
Query: 470 VVRNGHRLFVAA 481
Sbjct: 66 VERNGETITLTL 77
gnl|CDD|27588, cd00136, PDZ, PDZ domain, also called DHR
(Dlg homologous region) or GLGF (after a conserved sequence motif). Many
PDZ domains bind C-terminal polypeptides, though binding to internal
(non-C-terminal) polypeptides and even to lipids has been demonstrated.
Heterodimerization through PDZ-PDZ domain interactions adds to the
domain's versatility, and PDZ domain-mediated interactions may be
modulated dynamically through target phosphorylation. Some PDZ domains
play a role in scaffolding supramolecular complexes. PDZ domains are found
in diverse signaling proteins in bacteria, archebacteria, and eurkayotes.
This CD contains two distinct structural subgroups with either a N- or
C-terminal beta-strand forming the peptide-binding groove base. The
circular permutation placing the strand on the N-terminus appears to be
found in Eumetazoa only, while the C-terminal variant is found in all
three kingdoms of life, and seems to co-occur with protease domains. PDZ
domains have been named after PSD95(post synaptic density protein), DlgA
(Drosophila disc large tumor suppressor), and ZO1, a mammalian tight
junction protein. CD-Length = 70 residues, only 58.6% aligned
Score = 46.0 bits (109), Expect = 9e-06
Query: 313 DEGAGALVSEVLPGSPAANAGIQPGDVIRMVDGRTVRGASD 353
Sbjct: 10 GTEGGVVVLSVEPGSPAERAGLQAGDVILAVNGTDVKNLTL 50
gnl|CDD|27588, cd00136, PDZ, PDZ domain, also called DHR
(Dlg homologous region) or GLGF (after a conserved sequence motif). Many
PDZ domains bind C-terminal polypeptides, though binding to internal
(non-C-terminal) polypeptides and even to lipids has been demonstrated.
Heterodimerization through PDZ-PDZ domain interactions adds to the
domain's versatility, and PDZ domain-mediated interactions may be
modulated dynamically through target phosphorylation. Some PDZ domains
play a role in scaffolding supramolecular complexes. PDZ domains are found
in diverse signaling proteins in bacteria, archebacteria, and eurkayotes.
This CD contains two distinct structural subgroups with either a N- or
C-terminal beta-strand forming the peptide-binding groove base. The
circular permutation placing the strand on the N-terminus appears to be
found in Eumetazoa only, while the C-terminal variant is found in all
three kingdoms of life, and seems to co-occur with protease domains. PDZ
domains have been named after PSD95(post synaptic density protein), DlgA
(Drosophila disc large tumor suppressor), and ZO1, a mammalian tight
junction protein. CD-Length = 70 residues, 82.9% aligned
Score = 39.1 bits (91), Expect = 0.001
Query: 415 DGPGARVVVVAEGSVAAQAGLQPDDVIVALDQQPVTDVGQLLSI-LVKEHARALITVV 471
Sbjct: 11 TEGGVVVLSVEPGSPAERAGLQAGDVILAVNGTDVKNLTLEDVAELLKKEVGEKVTLT 68
 |
gnl|CDD|27595, cd00992, PDZ_signaling, PDZ domain
found in a variety of Eumetazoan signaling molecules, often in
tandem arrangements. May be responsible for specific protein-protein
interactions, as most PDZ domains bind C-terminal polypeptides, and
binding to internal (non-C-terminal) polypeptides and even to lipids
has been demonstrated. In this subfamily of PDZ domains an
N-terminal beta-strand forms the peptide-binding groove base, a
circular permutation with respect to PDZ domains found in proteases.
| CD-Length = 82 residues, only 51.2% aligned
Score = 45.6 bits (108), Expect = 1e-05
Query: 311 GIDEGAGALVSEVLPGSPAANAGIQPGDVIRMVDGRTVRGAS 352
Sbjct: 21 GKDSGGGIFVSRVEPGGPAERGGLRVGDRILEVNGVSVEGLT 62
 |
gnl|CDD|27594, cd00991,
PDZ_archaeal_metalloprotease, PDZ domain of archaeal zinc
metalloprotases, presumably membrane-associated or integral membrane
proteases, which may be involved in signalling and regulatory
mechanisms. May be responsible for substrate recognition and/or
binding, as most PDZ domains bind C-terminal polypeptides, and
binding to internal (non-C-terminal) polypeptides and even to lipids
has been demonstrated. In this subfamily of protease-associated PDZ
domains a C-terminal beta-strand forms the peptide-binding groove
base, a circular permutation with respect to PDZ domains found in
Eumetazoan signaling proteins. | CD-Length = 79 residues, only 53.2% aligned
Score = 44.1 bits (104), Expect = 3e-05
Query: 316 AGALVSEVLPGSPAANAGIQPGDVIRMVDGRTVRGASDVRRL 357
Sbjct: 10 AGVVIVGVIVGSPAENAVLHTGDVIYSINGTPITTLEDFMEA 51
 |
gnl|CDD|27591, cd00988, PDZ_CTP_protease, PDZ domain
of C-terminal processing-, tail-specific-, and tricorn proteases,
which function in posttranslational protein processing, maturation,
and disassembly or degradation, in Bacteria, Archaea, and plant
chloroplasts. May be responsible for substrate recognition and/or
binding, as most PDZ domains bind C-terminal polypeptides, and
binding to internal (non-C-terminal) polypeptides and even to lipids
has been demonstrated. In this subfamily of protease-associated PDZ
domains a C-terminal beta-strand forms the peptide-binding groove
base, a circular permutation with respect to PDZ domains found in
Eumetazoan signaling proteins. | CD-Length = 85 residues, only 45.9% aligned
Score = 42.9 bits (101), Expect = 8e-05
Query: 314 EGAGALVSEVLPGSPAANAGIQPGDVIRMVDGRTVRGAS 352
Sbjct: 11 DDGGLVITSVLPGSPAAKAGIKAGDIIVAIDGEPVDGLS 49
 |
gnl|CDD|25297, smart00228, PDZ, Domain present in
PSD-95, Dlg, and ZO-1/2. Also called DHR (Dlg homologous region) or
GLGF (relatively well conserved tetrapeptide in these domains). Some
PDZs have been shown to bind C-terminal polypeptides; others appear
to bind internal (non-C-terminal) polypeptides. Different PDZs
possess different binding specificities. | CD-Length = 86 residues, only 70.9% aligned
Score = 48.1 bits (114), Expect = 2e-06
Query: 313 DEGAGALVSEVLPGSPAANAGIQPGDVIRMVDGRTVRGASDVRRLVGSLPLQSKPSFQID 372
Sbjct: 24 SGDGGVVVSSVVPGSPAAKAGLKPGDVILEVNGTSVEGLTHLEAVDLLKEAGDKVTLTVL 83
Query: 373 R 373
Sbjct: 84 R 84
 |
gnl|CDD|25297, smart00228, PDZ, Domain present in
PSD-95, Dlg, and ZO-1/2. Also called DHR (Dlg homologous region) or
GLGF (relatively well conserved tetrapeptide in these domains). Some
PDZs have been shown to bind C-terminal polypeptides; others appear
to bind internal (non-C-terminal) polypeptides. Different PDZs
possess different binding specificities. | CD-Length = 86 residues, only 75.6% aligned
Score = 39.6 bits (92), Expect = 8e-04
Query: 412 NSPDGPGARVVVVAEGSVAAQAGLQPDDVIVALDQQPVTDVG--QLLSILVKEHARALIT 469
Sbjct: 22 KDSGDGGVVVSSVVPGSPAAKAGLKPGDVILEVNGTSVEGLTHLEAVDLLKEAGDKVTLT 81
Query: 470 VVRNG 474
Sbjct: 82 VLRGG 86
CD-Length = 217 residues, 75.1% aligned
Score = 54.3 bits (130), Expect = 3e-08
Query: 120 SGVVIDEVHGYIVTNQHVIASASKIEVAL-------SDGRRFQAKLVGA------DPET- 165
Sbjct: 27 GGSLISE--NWVLTAAHCVSGASSVRVVLGEHNLGLTEGTEQKFDVKKIIVHPNYNPDTN 84
Query: 166 DVAVVQIPPDH--------LVQAEFGSASSLHVGDVVVAIGNPFGLG-----QTATMGIV 212
Sbjct: 85 DIALLKLKSPVTLGDTVRPICLPSASSSLPVGTTCSVSGWGRTKNLGRSDTLQEVVVPVV 144
Query: 213 S-ALGRRAVGSEGYEGFIQTDA----STNPGNSGGALVSEDGVVV 252
Sbjct: 145 SRETCRSSYGGTVTDTMLCAGALGGKDACQGDSGGPLVCSDGELV 189
 |
gnl|CDD|25565, pfam00595, PDZ, PDZ domain (Also
known as DHR or GLGF). PDZ domains are found in diverse signaling
proteins. | CD-Length = 81 residues, only 48.1% aligned
Score = 43.0 bits (101), Expect = 7e-05
Query: 317 GALVSEVLPGSPAANAGIQPGDVIRMVDGRTVRGASDVR 355
Sbjct: 26 GIVVSEVLPGGAAERGGLKEGDRILEINGQDVENVTHER 64
gnl|CDD|10140, COG0265, DegQ, Trypsin-like serine
proteases, typically periplasmic, contain C-terminal PDZ domain
[Posttranslational modification, protein turnover, chaperones] CD-Length = 347 residues, 93.9% aligned
Score = 198 bits (504), Expect = 1e-51
Query: 40 LLALAALFIAGESLLSAPAVADS--LSLAPMLQRVVPSVVSISVQGRELDDADATLADPF 97
Sbjct: 8 DLAVGLLLIAAIAGGRALTSAAGQRLSFATAVEKVAPAVVSIATGLTAKLRSFFP----- 62
Query: 98 YRKFFGLPDDAAPAEHSFQSAGSGVVIDEVHGYIVTNQHVIASASKIEVALSDGRRFQAK 157
Sbjct: 63 ----------SDPPLRSAEGLGSGFIISSD-GYIVTNNHVIAGAEEITVTLADGREVPAK 111
Query: 158 LVGADPETDVAVVQIPPDHLVQA-EFGSASSLHVGDVVVAIGNPFGLGQTATMGIVSALG 216
Sbjct: 112 LVGKDPISDLAVLKIDGAGGLPVIALGDSDKLRVGDVVVAIGNPFGLGQTVTSGIVSALG 171
Query: 217 RRAVGSEG-YEGFIQTDASTNPGNSGGALVSEDGVVVGINSAIIGPAGGSIGIGFAVPAE 275
Sbjct: 172 RTGVGSAGGYVNFIQTDAAINPGNSGGPLVNIDGEVVGINTAIIAPSGGSSGIGFAIPVN 231
Query: 276 TVGIVMRQLILTGKLVRGEVGILTQDLTPGLAKAFGIDEGAGALVSEVLPGSPAANAGIQ 335
Sbjct: 232 LVAPVLDELISKGKVVRGYLGVIGEPLTADI--ALGLPVAAGAVVLGVLPGSPAAKAGIK 289
Query: 336 PGDVIRMVDGRTVRGASDVRRLVGSLPLQSKPSFQIDRASRRIE 379
Sbjct: 290 AGDIITAVNGKPVASLSDLVAAVASNRPGDEVALKLLRGGKERE 333
gnl|CDD|10140, COG0265, DegQ, Trypsin-like serine
proteases, typically periplasmic, contain C-terminal PDZ domain
[Posttranslational modification, protein turnover, chaperones] CD-Length = 347 residues, only 30.8% aligned
Score = 43.7 bits (102), Expect = 5e-05
Query: 380 AFPVVSDAPVAEPAAPRTIHIGRGPLADAEMANSPDGPGARVVVVAEGSVAAQAGLQPDD 439
Sbjct: 233 VAPVLDELISKGKVVRGYLGVIGEPLTADIALGLPVAAGAVVLGVLPGSPAAKAGIKAGD 292
Query: 440 VIVALDQQPVTDVGQLLSILVKEH--ARALITVVRNGHRLFVAADVQ 484
Sbjct: 293 IITAVNGKPVASLSDLVAAVASNRPGDEVALKLLRGGKERELAVTLG 339
 |
gnl|CDD|10661, COG0793, Prc, Periplasmic protease
[Cell envelope biogenesis, outer membrane] | CD-Length = 406 residues, only 11.8% aligned
Score = 44.6 bits (105), Expect = 2e-05
Query: 305 GLAKAFGIDEGAGALVSEVLPGSPAANAGIQPGDVIRMVDGRTVRGAS 352
Sbjct: 101 GIGIELQMEDIGGVKVVSPIDGSPAAKAGIKPGDVIIKIDGKSVGGVS 148
gnl|CDD|13280, COG3975, COG3975, Predicted protease with
the C-terminal PDZ domain [General function prediction only] CD-Length = 558 residues, only 18.6% aligned
Score = 40.3 bits (94), Expect = 4e-04
Query: 303 TPGLAKAFGIDEGAGALVSEVLPGSPAANAGIQPGDVIRMVDGRTVRGASDVRRLVGSLP 362
Sbjct: 450 AYYLGLKVK-SEGGHEKITFVFPGGPAYKAGLSPGDKIVAINGISDQ--------LDRYK 500
Query: 363 LQSKPSFQIDRASRRIEAFPVVSDAPVAEPAAPRTIHIGRGPLADAEMANSPDGPGAR 420
Sbjct: 501 VNDKIQVHVFREGRLRE-FLVKLGG----DPTAQYIILPIGDRNPAQLANAAAWLGEI 553
gnl|CDD|10618, COG0750, COG0750, Predicted
membrane-associated Zn-dependent proteases 1 [Cell envelope biogenesis,
outer membrane] CD-Length = 375 residues, only 26.1% aligned
Score = 39.8 bits (92), Expect = 7e-04
Query: 306 LAKAFGIDEGAGALVSEVLPGSPAANAGIQPGDVIRMVDGRTVRGASDVRRLVGSLPLQS 365
Sbjct: 119 LFFVIGLVPVASPVVGEVAPKSAAALAGLRPGDRIVAVDGEKVASWDDVRRLLVAAAGDV 178
Query: 366 KPSFQIDRASRRIEAFPVVSDAPVAEPAAPRTIHIGRG 403
Sbjct: 179 FNLLTILVIRLDGEAHAVAAEIIKSLGLTPVVIPLKPG 216
Citing
CD-Search: Marchler-Bauer A, Anderson JB, DeWeese-Scott C,
Fedorova ND, Geer LY, He S, Hurwitz DI, Jackson JD, Jacobs AR, Lanczycki
CJ, Liebert CA, Liu C, Madej T, Marchler GH, Mazumder R, Nikolskaya AN,
Panchenko AR, Rao BS, Shoemaker BA, Simonyan V, Song JS, Thiessen PA,
Vasudevan S, Wang Y, Yamashita RA, Yin JJ, and Bryant SH (2003), "CDD:
a curated Entrez database of conserved domain alignments", Nucleic
Acids Res. 31:383-387. |

 ..
This CD alignment includes 3D structure. To display structure, download
Cn3D!
..
This CD alignment includes 3D structure. To display structure, download
Cn3D!